Agricultural Mapping Using Satellite Imagery for Irrigation Water Usage Planning
Determine the most cost effective techniques to use remote sensing for agricultural mapping for water use estimation.
• Specific requirements are:
– high classification accuracy for all crops present each season
– high accuracy of area estimation of each crop
• Area of each crop to be measured each year for the calculation of agricultural water needs for irrigation management.
Resources Provided for Analysis
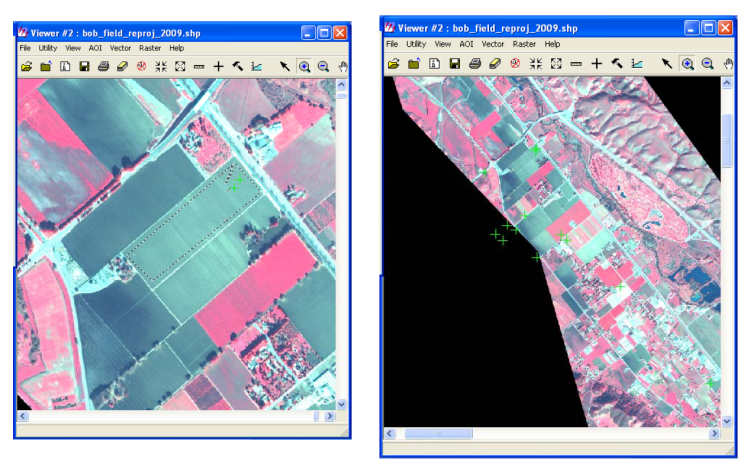
• 4 band Quickbird imagery pan‐sharpened to 60cm for a specific area of emphasis.
• 56 GPS points with varying descriptions of crops with no field metadata and 1‐3 points per crop
• Unlabeled pictures of each GPS point.
• Zoning parcels for the county (though not all GPSed fields fall within an Ag. parcel)
• All analysis done on Erdas Imagine 9.0
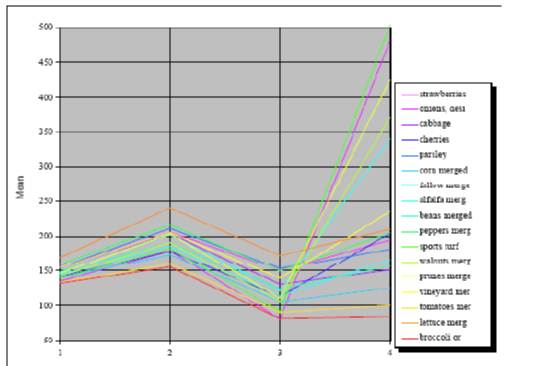
Quickbird Classification Accuracy Assessments
• AOI Ag Parcels Only
– 23.53 % overall accuracy for Ag parcels only
– Overall Kappa Statistics = 0.2095
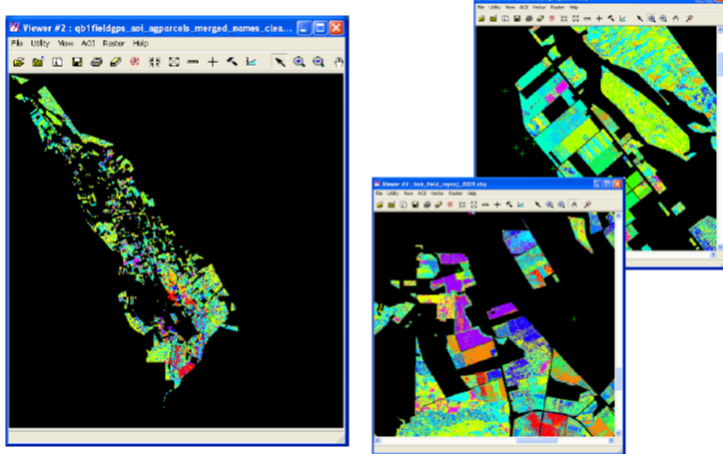
Repeating Classification Techniques with Free LandSat 5 Imagery
• Loss of Spatial Resolution from 60cm to 30m (pan‐sharpening of LandSat not completed)
• Increase of Spectral Information from 4 to 7 bands with improved NIR and SWIR coverage.
• Greater Spatial Coverage Including All Field GPS Data Already Collected
• Greatly reduced computation and data storage requirements for repeat analyses
• Price Savings of $15, 200 per image.
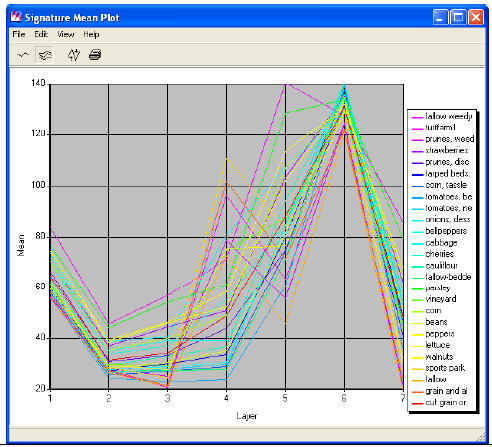
Classification Accuracies for Landsat 5
• All Image, 26 classes tested
– Overall Classification Accuracy = 80.77%
– Overall Kappa Statistics = 0.7987